Negative Working Capital Formula + Calculator
Content
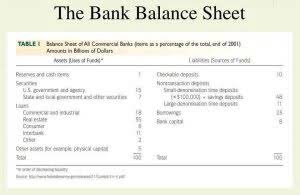
Inventories (often also called “stocks”) are the least liquid kind of current asset. Inventories include holdings of raw materials, components, finished products ready to sell and also the cost of “work-in-progress” as it passes through the production process. Current assets are listed in order of their liquidity – or in other words, how easy it is to turn each category of current asset into https://www.bookstime.com/articles/accounting-automation cash. Noncurrent assets are depreciated in order to spread the cost of the asset over the time that it is used; its useful life. Noncurrent assets are not depreciated in order to represent a new value or a replacement value but simply to allocate the cost of the asset over a period of time. The return on equity measures how much profit a business generates from shareholders’ equity.
The more liquid assets that a company has, the less trouble it will have paying its operating expenses and bills. Liquid assets also make companies more flexible, making it easier for them to quickly invest funds in new projects. Things like factory equipment, real estate, or technological patents are all assets. For instance, selling real estate can easily take months, which means that a company couldn’t easily sell some land to pay a bill. That lack of ability to sell an asset to cover an immediate expense is what makes an asset non-liquid.
What Is the Difference Between a Fixed Asset and a Noncurrent Asset?
Companies use liquidity ratios to measure working capital performance – the money available to meet your current, short-term obligations . Liquid assets matter because they represent a company’s ability to pay for its expenses without having to sell off larger parts of its business. Solvency ratios are a popular way for investors to get a quick idea of a company’s financial situation. Just as a company’s PE ratio compares a stock’s price and earnings, solvency ratios compare a company’s assets and liabilities.
Financial ratios are sometimes referred to as accounting ratios or finance ratios. These ratios are important for assessing how a company generates revenue and profits using business expenses and assets in a given period. Internal and external stakeholders use financial ratios for competitor analysis, market valuation, benchmarking, and performance management.
Managing Your Current Assets
Current assets are usually presented first on the company’s balance sheet and they are arranged in their order of liquidity. This can help a company improve its financial health and avoid defaulting on its loans. Now that we know what current assets are, let’s explore some of the different types in more detail. It simplifies the process of optimizing your asset operations to help you increase uptime, extend the life of your equipment, and make your business’s assets more efficient and valuable. You can all too easily record lost, damaged, or stolen assets in your business’s books.
Is inventory a current asset?
Inventory is regarded as a current asset as the business as it includes raw materials and finished goods that can be converted into cash within one year or less.
Both assets and liabilities are broken down into current and noncurrent categories. Cash and cash equivalents – This is actual currency that’s available for use. Cash equivalents are short-term current assets business definition investments that will mature, or become cash, within no more than three months. For the purposes of this lesson, we will only be discussing the current assets subsection of the balance sheet.
What is Negative Working Capital?
Some examples of current assets include cash, cash equivalents, short-term investments, accounts receivable, inventory, supplies, and prepaid expenses. The current ratio is a metric used by accountants and finance professionals to understand a company’s financial health at any given moment. This ratio works by comparing a company’s current assets (assets that are easily converted to cash) to current liabilities (money owed to lenders and clients). Intangible assets are nonphysical assets, such as patents and copyrights. They are considered noncurrent assets because they provide value to a company but cannot be readily converted to cash within a year.
